sludge centrifugation suitability
Reading time:When a sample of sewage fresh mixed sludge is subjected to a 2,000 g centrifugal field for a few minutes in a laboratory centrifuge, we will find the following in the centrifuge pot (figure 29):
- cloudy supernatant liquid;
- bottom sediment featuring two main areas:
- one lower and fairly hard zone (DM = 25-35 %);
- one upper and extremely pasty zone (DM = 10-15 %) with a high OM content.
If the same experiment is repeated with sludge that has been flocculated using a polyelectrolyte, we find:
- a clarified supernatant liquid;.
- a homogenous sediment having an intermediate dry solids content (DM = 18-22 %) and good cohesion.

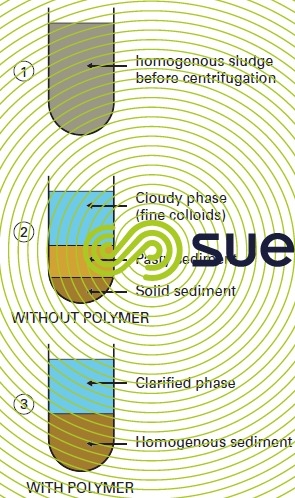

This capacity of a sludgy suspension for separating into two distinct phases when a centrifugal force is applied (therefore, without the barrier formed by a filtering medium as would be the case with a belt filter or a filter press), expresses sludge «centrifugability».
Polymer conditioning is essential to obtaining a good solid-liquid separation.
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later