estimated water pollution during rainfall
Reading time:Overflows from the combined system or even from separate systems, excess water that occurs during a rainfall episode will discharge significant quantities of pollution into the natural environment and, when a water treatment plant deals normally with dry weather water, this excess water can become a major contributor of pollution to the natural environment. This can be seen from tables 32 and 33 that provide examples from the Paris (France) region.
If we wish to improve this situation, we can:
- either process said excess water as it occurs (see examples of typical water treatment lines) e.g. physical-chemical treatment;
- or store the water and send it at reduced flows to the purification plants.




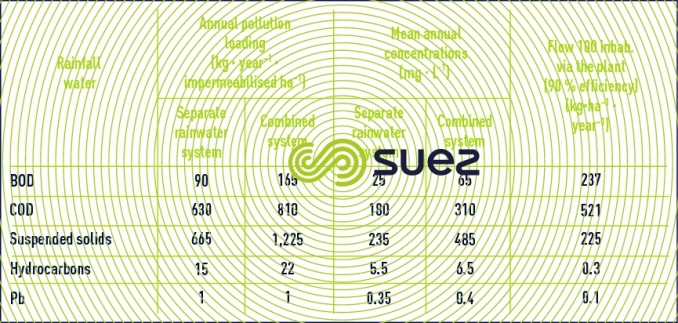

It should be noted that run-off water mainly contains suspended solids (leached from impermeabilised soils) and it can be said that approximately 85% of COD and BOD, 70% of nitrogen (NK), 90% of hydrocarbons and over 95% of metals (Pb, Zn, Cu) will be present as particulates.
Similarly, run-off water usually contains more metals, especially Pb, Zn, Cd cause by rusting roofs, downpipes, tyre wear, hydrocarbon combustion residues… These residues also contribute to microbial pollution (leaching of animal manure in particular) and, during the first hours of a rain storm, separate systems reveal concentrations that are close to those found in wastewater in dry weather for instance. 108 total coliforms·100 mL–1.
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later