suspended solids ( SS ) in liquid sludge
Reading time:When a sludge is not concentrated, the dry weight should not include the dis- solved substances contained in the sludge interstitial water. Two possible methods exist to determine the SS.
the centrifugation method
This procedure uses a laboratory centrifuge equipped with 100 mL graduated scoops. Each scoop is filled with 80 mL of sludge and centrifuged at 4,000-5,000 rpm for 10 minutes. At the end of this operation, the supernatant liquor is removed and all sludge pellets are carefully collected and allowed to dry out at 105°C in an oven until a constant mass is achieved (this usually takes at least 12 hours).
Note: Preliminary flocculation of the sludge using a few mg· L-1of polymer (flocculation carried out in situ in the scoop) will produce homogenous pellets of sludge that can be easily collected without loosing any matter. If M(g) is the mass of residual dry solids obtained and V (mL) the volume of sludge centrifuged (V = 160 or 320 mL).

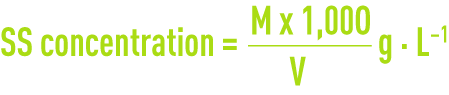
filtration method
This method is typically conducted for sludges with low SS concentrations (e.g. 2 to 10 g · L–1).
Precisely calibrate a filter paper (extra rapid ash-free filter type Ø150, Durieux for example) and filter the sludge (25 to 100 mL depending on concentration) over a glass funnel. This method can be complicated with sludges having poor filtering properties. Filters are thereafter dried in an oven at 105°C until a steady mass is achieved.

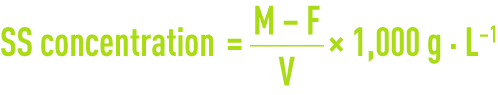
where:
M: dry mass of the filter and of the cake (g),
F: mass of the filter only (g),
V: volume of sludge filtered (mL).
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later