customary, definitions and formulae
Reading time:direct current
intensity

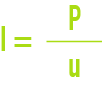
resistance

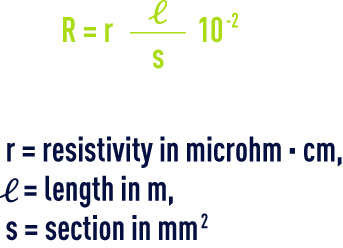
alternating current
power factor or cos Ø
Intensity and an alternating current voltage will rarely be in phase. The cosinus of the angle formed by the two intensity voltage vectors is called the power factor.
When a self-induction is incorporated into a circuit, it steps the intensity back from the voltage; when a capacitance is incorporated, it has the opposite effect.
The active power is decreased in both cases (figure 45).
In the case of an industrial sinusoidal current (general case) :
- Ia = I cos Ø is the active current;
- Ir = I sin Ø is the reactive current.

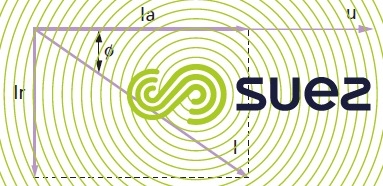

apparent, active, reactive power
I is the intensity read on an ampere metre, U the main voltage between phases, for a three phase supply.
u is the mains voltage between phase and neutral, for a single phase supply, power is detailed in table 75.



The apparent power is expressed in volt-amperes (VA).
The active power is expressed in Watts (W).
The reactive power is expressed in reactive volt-amperes (VAr).
A poor cos Ø is detrimental to both the energy user and to the energy supplier. It requires large conduit sections and higher apparent power levels for alternators and transformers.
circuit impedance
Circuit impedance is the resultant of the ohmic resistance and the circuit’s reactance.


R = resistance,
X = reactance (inductive, capacitive).
Amount of heat given off by a circuit having a resistance R and crossed by a current I for one second.

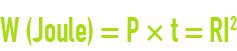
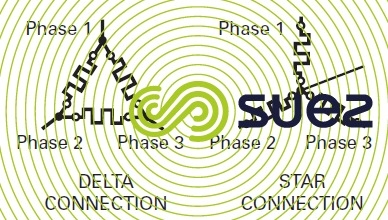
star and delta connections
Resistances and motor windings can be connected in star or delta configuration. Figure 46 recaps the characteristics of both these configurations.


Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later