flocculation with sludge contact
Reading time:If we include the differential equations that apply to orthokinetic flocculation, see section general comments, we obtain the following equation:

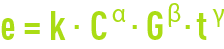
that expresses flocculation effectiveness, where
e: parameter associated with the floc formed (size, settleability, filtration capacity …) or with the quality of the clarified water.
C: sludge concentration in the flocculation tank.
G. velocity gradient.
t: contact time.
α, β, γ >0.
In general, the increased contact mass (C) leads to an increase in the probability of collision taking place inside the tank, and in more effective flocculation.
Sludge contact equipment, creating or injecting a larger amount of sludge into the flocculation zone, is based on this principle.
Two different methods are used (see also section sludge contact clarification):
- sludge recirculation: an integrated or external system continuously feeds concentrated sludge arriving from the floor of the sedimentation tank into the flocculation zone;
- the sludge blanket: in an upflow structure, a balance will be established between the velocity of the water and the hindered settling rate of flocculated particles. Once flocculated particles have reached a certain concentration, a sludge blanket will be created, acting as both flocculator and "fluidised filter", producing excellent flocculation; in addition sedimentation is optimised accordingly.
Sludge contact offers a range of advantages:
- improved flocculation rate;
- no fine particles, homogenous floc;
- accelerated settling rate and, therefore, smaller structures accordingly;
- completion of specific reactions (precipitation, adsorption over powdered activated carbon …);
- enhanced organic matter removal through adsorption over floc;
- savings on chemical reagents (improved use of reagents, coagulant and flocculating effect of recycled sludge).
The scope of flocculation with sludge contact is immense: clarification, specific precipitations (carbonate removal, silicon removal…), colour removal, iron or manganese removal, clarification as part of pre or post treatment in aerobic or anaerobic biological water purification treatment.
Note: when the sludge concentration in the reactor is too high, this will have a limiting effect on the sedimentation rate.
The section sedimentation and the chapter flocculators – settling tanks – flotation units illustrate the importance of these concepts.
Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later