biological treatment
Reading time:The most efficient biological treatment will be selected on the basis of a range of factors:
- required discharge water quality standards that may dictate two biological stages;
- initial COD concentration, a COD > 2 g·L–1 that will make it financially possible to consider processes such as methane fermentation, Ultrafor or high-load aerobic treatment;
- the seasonal variability of the wastewater, generally requiring a two-stage high-load + low-load treatment;
- whether nitrogen removal is required (often an important factor);
- requirement for phosphate removal (typical of dairy and meat industries) and, in such cases, high levels of easily biodegradable BOD dictate biological phosphate removal (see suspended growth (activated sludge) process);
- space limitations: anaerobic, Méteor, Ultrafor, Biofor;
- sludge disposition which may necessitate minimum sludge production: methane fermentation, Ultrafor, or even activated sludge with reduced sludge output (Biolysis E or O, Biocontrol).
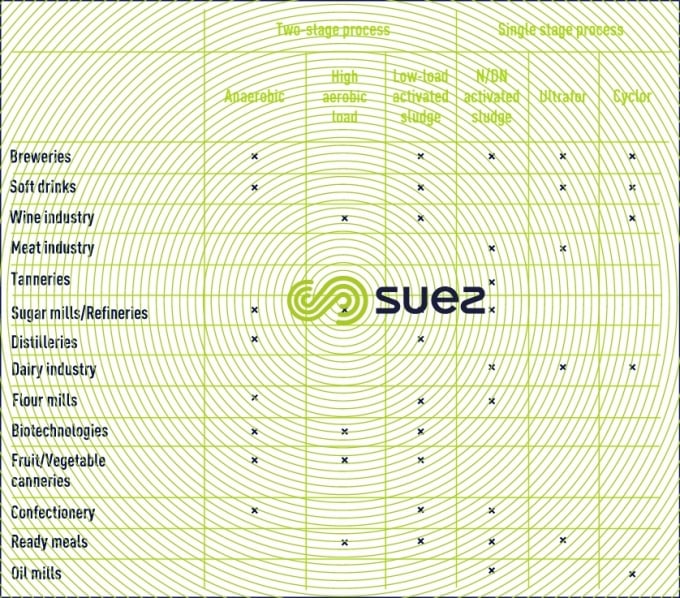
Table 3 provides a general summary of the most commonly-found processes for each type of industry.


Bookmark tool
Click on the bookmark tool, highlight the last read paragraph to continue your reading later